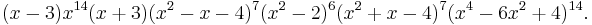Ljubljana graph
| Ljubljana graph | |
|---|---|
The Ljubljana graph is hamiltonian. |
|
| Vertices | 112 |
| Edges | 168 |
| Radius | 7 |
| Diameter | 8 |
| Girth | 10 |
| Automorphisms | 168 |
| Chromatic number | 2 |
| Chromatic index | 3 |
| Properties | Cubic Semi-symmetric Hamiltonian |
In the mathematical field of graph theory, the Ljubljana graph is an undirected bipartite graph with 112 vertices and 168 edges.[1]
It is a cubic graph with diameter 8, radius 7, chromatic number 2 and chromatic index 3. Its girth is 10 and there are exactly 168 cycles of length 10 in it. There are also 168 cycles of length 12.[2]
Contents |
Construction
The Ljubljana graph is Hamiltonian and can be constructed from the LCF notation : [47, -23, -31, 39, 25, -21, -31, -41, 25, 15, 29, -41, -19, 15, -49, 33, 39, -35, -21, 17, -33, 49, 41, 31, -15, -29, 41, 31, -15, -25, 21, 31, -51, -25, 23, 9, -17, 51, 35, -29, 21, -51, -39, 33, -9, -51, 51, -47, -33, 19, 51, -21, 29, 21, -31, -39]2.
The Ljubljana graph is the Levi graph of the Ljubljana configuration, a quadrangle-free configuration with 56 lines and 56 points.[2] In this configuration, each line contains exactly 3 points, each points belongs to exactly 3 lines and any two lines intersect in at most one point.
Algebraic properties
The automorphism group of the Ljubljana graph is a group of order 168. It acts transitively on the edges the graph but not on its vertices : there are symmetries taking every edge to any other edge, but not taking every vertex to any other vertex. Therefore, the Ljubljana graph is a semi-symmetric graph, the third smallest possible cubic semi-symmetric graph after the Gray graph on 54 vertices and the Iofinova-Ivanov graph on 110 vertices.[3]
The characteristic polynomial of the Ljubljana graph is
History
The Ljubljana graph was first published in 1993 by Brouwer, Dejter and Thomassen.[4]
In 1972, Bouwer was already talking of a 112-vertices edge- but not vertex-transitive cubic graph found by R. M. Foster, but unpublished.[5] Conder, Malnič, Marušič, Pisanski and Potočnik rediscovered this 112-vertices graph in 2002 and named it the Ljubljana graph after the capital of Slovenia.[2] They proved that it was the unique 112-vertices edge- but not vertex-transitive cubic graph and therefore that was the graph found by Foster.
Gallery
References
- ^ Weisstein, Eric W., "Ljubljana Graph" from MathWorld.
- ^ a b c Conder, M.; Malnič, A.; Marušič, D.; Pisanski, T.; and Potočnik, P. "The Ljubljana Graph." 2002. [1].
- ^ Marston Conder, Aleksander Malnič, Dragan Marušič and Primž Potočnik. "A census of semisymmetric cubic graphs on up to 768 vertices." Journal of Algebraic Combinatorics: An International Journal. Volume 23, Issue 3, pages 255-294, 2006.
- ^ Brouwer, A. E.; Dejter, I. J.; and Thomassen, C. "Highly Symmetric Subgraphs of Hypercubes." J. Algebraic Combinat. 2, 25-29, 1993.
- ^ Bouwer, I. A. "On Edge But Not Vertex Transitive Regular Graphs." J. Combin. Th. Ser. B 12, 32-40, 1972.